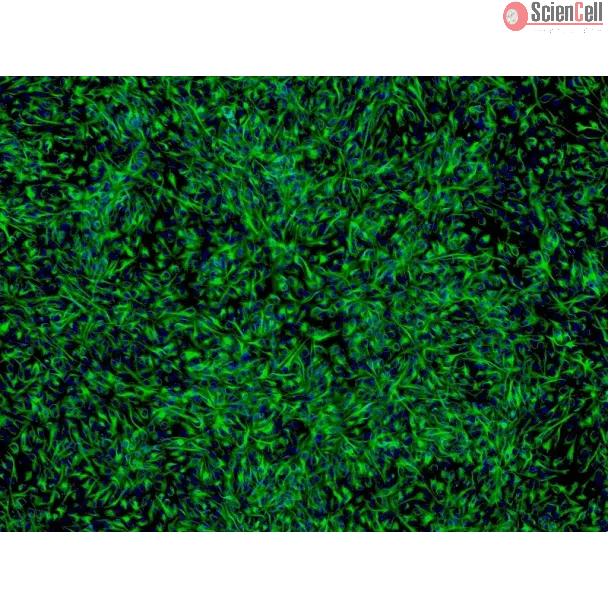
Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
Isolated from human retina. HRPEpiC are cryopreserved at passage one and delivered frozen. Each vial contains >5 x 105 cells in 1 ml volume.
Limited Availability and Promotions cannot be applied to this product.
Related Products
Check items to add to the cart or




,-1-mg-ml--2.jpg)