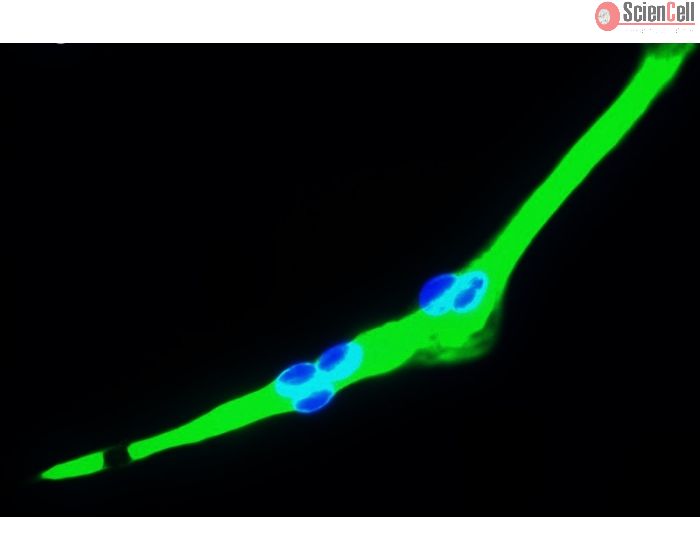
Human Skeletal Muscle Cells
Catalog No.
3500
Isolated from human trapezius muscle and erector spinae muscles of the back. HSkMC are cryopreserved at passage one and delivered frozen. Each vial contains >5 x 105 cells in 1 ml volume.
$831.00
In Stock
Related Products
Check items to add to the cart or