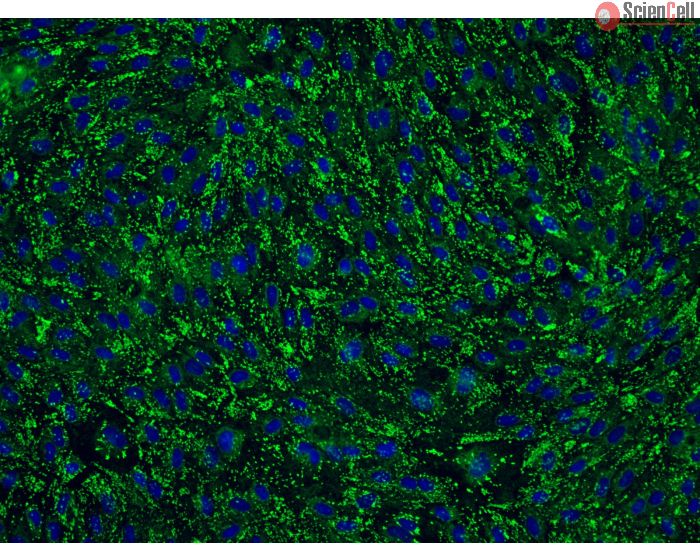
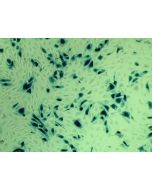
Human Cervical Microvascular Endothelial Cells
Catalog No.
7050
HCerMEC from ScienCell Research Laboratories are isolated from human cervix. HCerMEC are cryopreserved at passage one and delivered frozen. Each vial contains >5 x 105 cells in 1 ml volume.
$839.00
In Stock
Related Products
Check items to add to the cart or