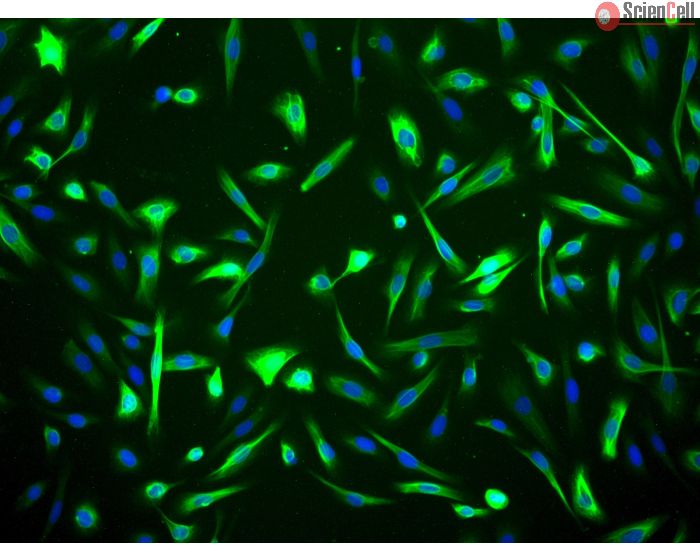
Human Mammary Epithelial Cells
Catalog No.
7610
Isolated from human breast. HMEpiC are cryopreserved at passage one and delivered frozen. Each vial contains >5 x 105 cells in 1 ml volume.
Read published article here: http://bit.ly/SC7610
(Effects of chemically modified nanostructured PLGA on functioning of lung and breast cancer cells)
$736.00
In Stock
Related Products
Check items to add to the cart or